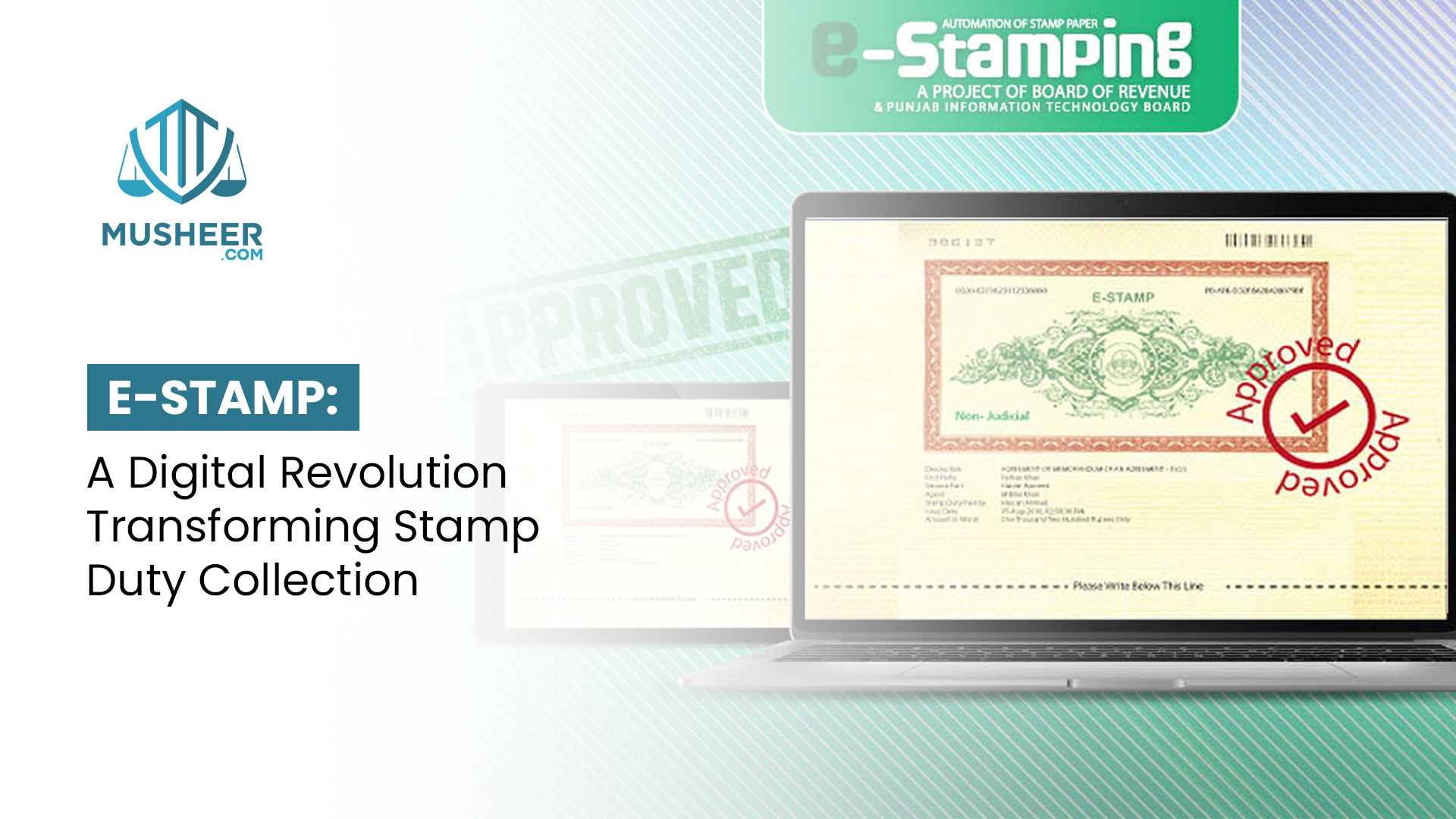
Filing a civil suit in Pakistan can be complicated and stressful, but it doesn't have to be. By understanding the process and the rules involved, you can make filing a civil suit an easier process. This comprehensive guide will provide all the necessary information you need to know about filing civil suits in Pakistan. From the initial paperwork to the court proceedings, this guide will help you navigate the entire process with ease.
7 Steps In A Civil Suit Process
Step 1: Prepare The Plaint
Filing a plaint in the Court is the first step to formally starting your suit. The plaint is a formal legal document that outlines the facts of your case, the legal basis for your claim, and the relief you are seeking.
It is important to ensure that your plaint is drafted correctly and includes all necessary information. If the complaint is deficient in any way, it may be dismissed by the court. A knowledgeable lawyer can provide essential guidance, assess the merits of your case, help you navigate the legal complexities ahead, and prepare a well-structured plaint that accurately presents your case.
Step 2: Determine The Proper Venue For The Case
A suit can only be filed in a Court having jurisdiction on the subject. The jurisdiction of the Court is determined based on the subject matter of the dispute or the geographical location of the parties involved.
In Pakistan, civil cases are heard by civil judges in district courts. The district court that has jurisdiction over your case will depend on where the cause of action arose or where the defendant resides
Step 3: File The Plaint
After determining the proper venue, the next step is to file the plaint.
The plaint is to be submitted in the appropriate Court along with the required number of copies. Pay the prescribed filing fee, which varies depending on the nature and value of the claim.
Step 4: Serve The Defendant
Once the plaint has been filed, the next step is to serve the defendant with a copy of the plaint and a summons. Proper service of this notice to the defendant is essential. Service to defendant must be done in accordance with the rules of civil procedure.
The defendant will then have a certain amount of time to respond to the plaint. If they fail to do so, a default judgment may be entered against them.
Step 5: The Defendant's Response
After the defendant receives the notice, he will file his Written Statement in the Court. The Written Statement is a document filed by the defendant in response to a plaint (the initial claim) filed by the plaintiff in a civil suit. It is an important legal document that allows the defendant to present their version of the facts, raise defenses, and respond to the claims made by the plaintiff.
Step 6: Going To Trial
After the defendant files his written statement, the court will schedule hearings and proceedings according to its docket. Both parties will be represented by their lawyers who will present arguments, submit evidence, and cross-examine witnesses if required.
Step 7: Judgement
The court will deliver a judgment following the conclusion of arguments and evidence. If a party is dissatisfied with the decision, they have the option to file an appeal within the specified timeframe. The appellate court will review the case, and depending on its findings, may uphold, modify, or overturn the lower court's decision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the process of filing a civil suit in Pakistan is essential for individuals seeking legal recourse in matters of a civil nature. Navigating the legal system can be complex, but by following the steps outlined in this article and seeking professional legal advice, individuals can effectively initiate a civil suit.